What is Antibiotic Potency Testing?
Antibiotic Potency Testing is a biological assay used to determine the potency (concentration) of antibiotic active pharmaceutical ingredients (API’s) and the products which contain them.
FDA requires that the potency of antibiotic drug products conform to the potency appearing on their labeling in order to be distributed within the United States. USP General Chapter <81> entitled “Antibiotic Potency Assays” provides validated methods for determining the potency of multiple antibiotic active ingredients based upon their actions against specific microorganisms.
For the highest quality testing, antibiotic potency assessments should be performed by qualified personnel with expertise in microbiology and aseptic techniques as well as analytical biological methods. CPT Labs performs all antibiotic potency testing according to validated procedures outlined in USP <81> Antibiotics—Microbial Assays. USP <81> is the primary and most commonly used reference document for biological antibiotic potency evaluations.
How is Antibiotic Potency Testing Conducted?
USP General Chapter <81> entitled “Antibiotic Potency Assays” provides method types for determining antibiotic potency. CPT performs the Cylinder-Plate Assay for the antibiotics indicated in USP <81>.
Cylinder-Plate Assay:
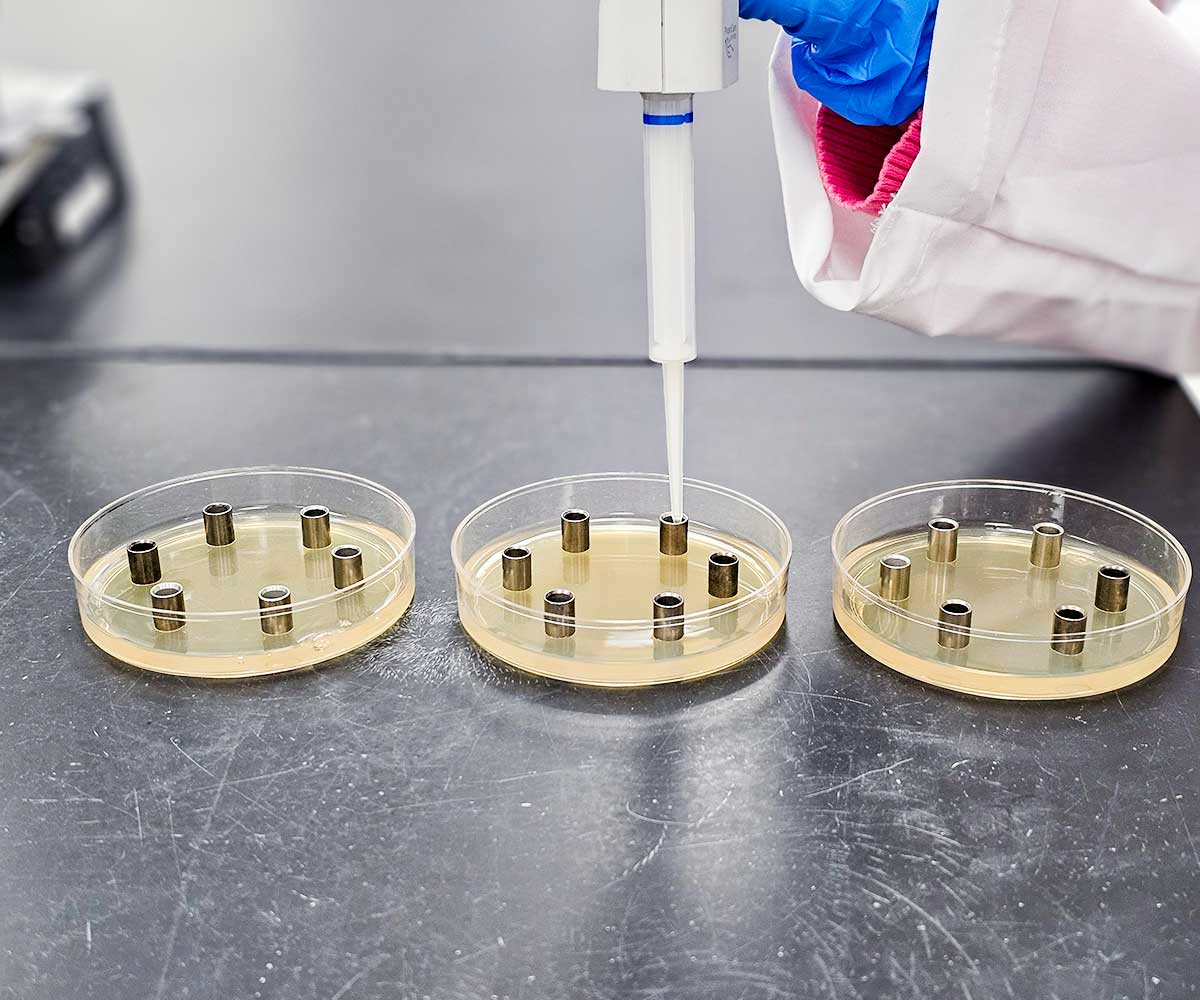
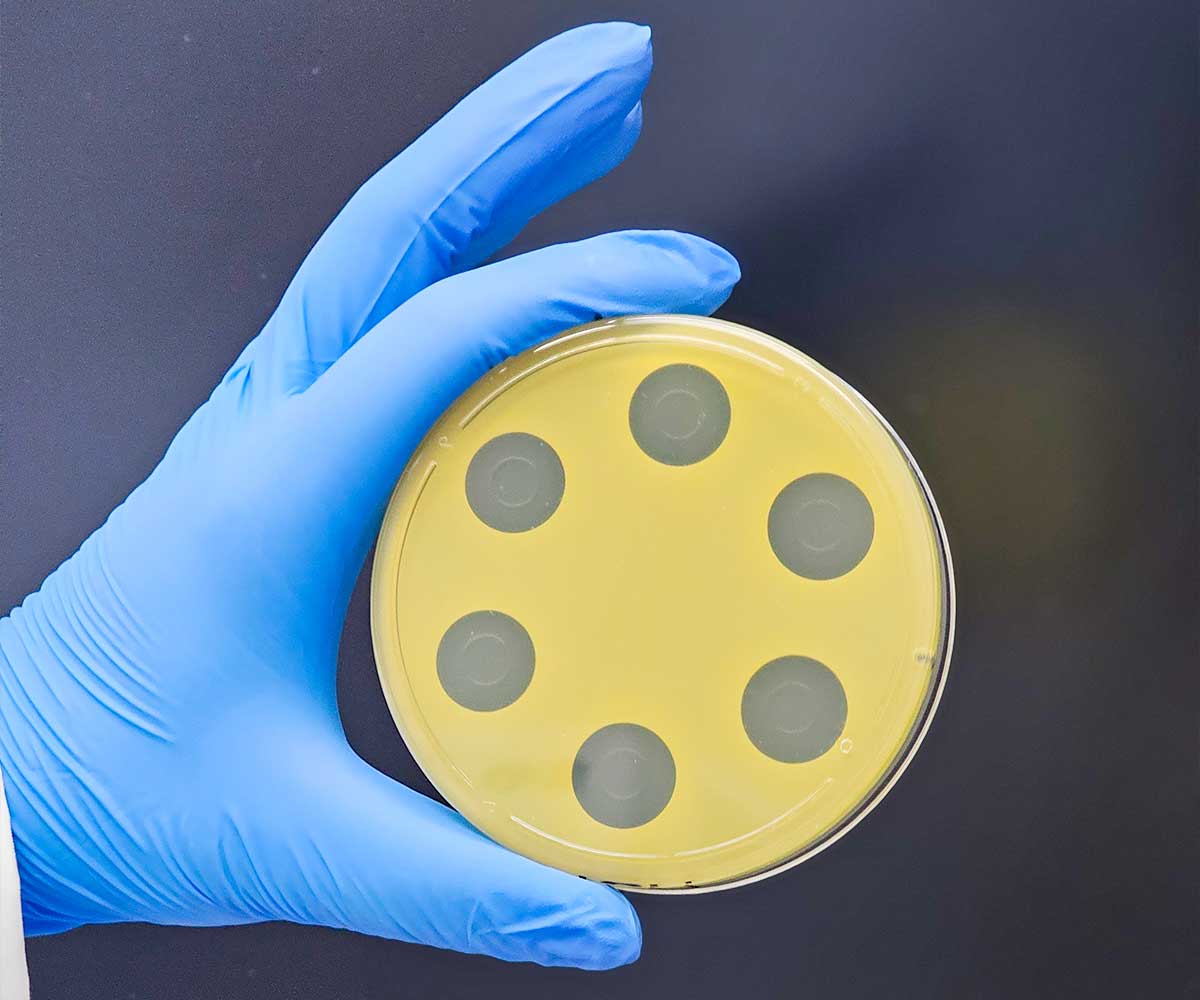
This antibiotic potency test extracts the antibiotic active ingredient(s) from the product being tested using solvents and phosphate buffers as outlined in USP <81>. After extraction, the sample preparations are diluted to the median dose of the active ingredient that is found on a Standard curve which is created for the analysis.
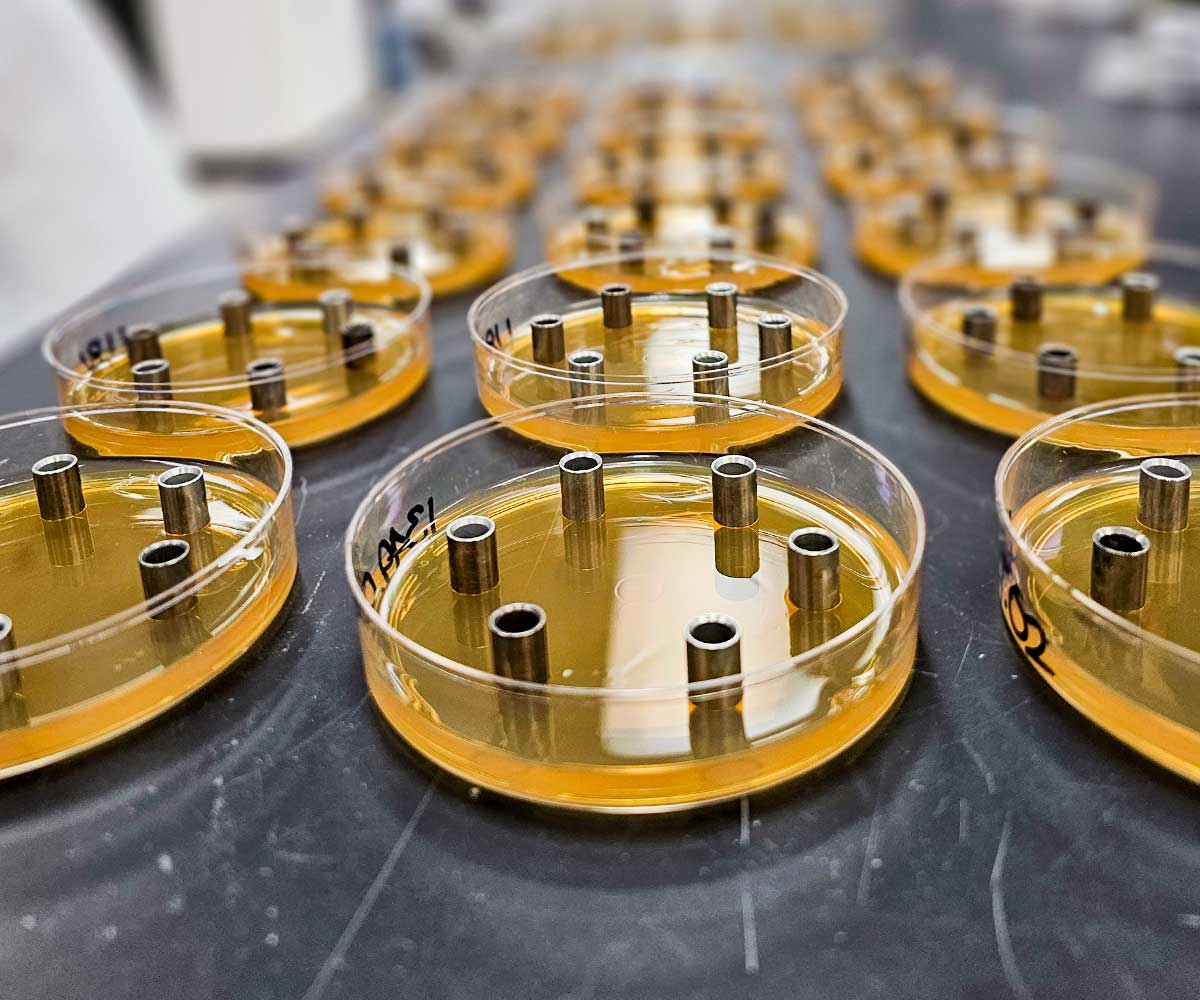
The sample and corresponding USP Reference Standard preparations are pipetted into penicylinders that are placed into a petri dish already containing a base layer of antibiotic growth medium and a seed layer of antibiotic growth medium which also contains a USP-specified microorganism that is sensitive to the antibiotic being tested.
The plates containing the cylinders are then incubated as specified within the method. The Cylinder-Plate Assay is based upon the ability of the antibiotic being assayed and its corresponding Reference Standard to diffuse through the agar and form a ‘zone of clearing’ (‘zone of inhibition’) thereby killing the microorganism which was present within the seed media.
The ‘zone’ sizes are measured (in millimeters) using either an automated zone reader or manually using either calibrated calipers or a manual antibiotic zone reader. The size of each ‘zone’ is proportional to the quantity of antibiotic present. Results are calculated using a formula comparing the size of the ‘zone’ obtained from known quantities of antibiotic contained in the Reference Standard to the size of the ‘zone’ obtained from the sample. The Cylinder-Plate Assay is performed by conducting three independent assays on three different days.
USP <81> lists 18 antibiotics that require the use of the cylinder plate assay for the antibiotic raw materials and the Finished Products. Some of the most common performed at CPT include Neomycin sulfate, Bacitracin zinc, Polymyxin B Sulfate, Nystatin, Amphotericin B, Gentamicin sulfate, and Erythromycin.
Other antibiotics which require the cylinder plate assay are Amoxicillin, Bleomycin, Cloxacillin, Colistemethate, Colistin, Dihydrostreptomycin, Nafcillin, Novobiocin, Paromomycin, Penicillin G and Vancomycin.